Key takeaways
- Role of AI-driven software: Intelligent applications use AI to provide real-time insights, automate processes, and enhance decision-making.
- Future standards: IA will enhance disruption response by automating routine tasks and coordinating preventive actions
- Examples and use cases: IAs optimize resource management, predicting and resolving maintenance issues efficiently and across various sectors.
- Key considerations: Ensure scalable AI infrastructure, responsible AI practices, user feedback integration, and strong data governance.
Disruptive events, such as production delays, extreme weather, and geopolitical supply chain risks, cost global businesses over $1 trillion annually. The market for disruption prevention has grown rapidly, offering predictive data, remote maintenance, and AI-driven autonomous responses. While these preventive solutions provide powerful capabilities, they also increase operational complexity with the number of applications workers must learn and leverage during disruption prevention and response.
The Role of Intelligent Applications in disruption prevention and response
Intelligent apps, also known as smart applications or AI apps, offer a number of capabilities and benefits, allowing organizations to leverage AI, machine learning, remote sensing, data analytics and more to gain real-time insights, automate processes, and enhance decision-making across IT ecosystems. In disruption prevention and response, IAs play a crucial role by integrating and coordinating disparate systems, enabling predictive maintenance, and facilitating autonomous responses to potential issues. They improve the user experience by simplifying complex data interactions, providing actionable insights, and creating seamless feedback loops, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. Intelligent apps can also monitor network traffic to identify unusual spikes that could indicate issues, providing early detection of potential problems before they escalate.
As an example, an employee notices that several lightbulbs have burned out in a main stairwell at a nearby facility. To resolve this, the employee opens a ticket with the maintenance team, who is working through their tickets sequentially as they are received. The maintenance team, once they get to this specific ticket, assesses they need to visit the location described, determine which bulbs should be replaced (or only tightened), and then complete the work required for the ticket’s resolution. This requires information from inventory (bulbs), equipment (scissor-lift), and personnel to complete. What the ticket doesn’t show is the additional 25 bulbs that are past their end-of-life dates, and that the scissor-lift required for maintenance is being used for another task for the rest of the day. Instead of resolving inefficiencies as they arise, IA can aggregate, coordinate, and optimize resources so that one person can solve 25 tickets in one afternoon, rather than solving them one-by-one. In the future, IA can also start to predict daily maintenance workloads, which makes it easier to justify hiring additional personnel, optimize schedules, and time procurement for needed parts.
While overly simplified, this simple example illustrates how the power of coordinated response across machinery, servers, and applications can minimize disruptions to business operations. This is the power of IA.
The rise of intelligent applications: Does your technology ecosystem integrate, coordinate, and learn?
Disruption prevention and response standards today are a hybrid of digital and manual capabilities. Remote sensing can provide notice for a maintenance need, resolved with a manual fix. However, the underlying challenge remains the same-prediction and response are not closely coordinated, with a missing feedback loop between repair and future preventive action.
The coming wave of IA offerings will require the integration of the preventive capability ecosystem. This includes the coordination of resource and asset responses, and learning from workforce action and feedback loops. Beginning in 2024 and accelerating in 2025, IA is predicted to play a central role in enterprise IT planning.
How intelligent applications evolve early detection, disruption prevention, and response
Many IT companies operate by firefighting a continuous stream of disruptions, becoming trapped in a loop of responding to events and implementing point solutions. As disruption complexity rises, so does the technology ecosystem, creating a persistent gap between expanding preventive capabilities and the technology ecosystem required for a cohesive response.
Intelligent apps can assist with capacity planning and making informed decisions by using historical data to predict future trends and manage systems efficiently. Additionally, these applications can improve performance by keeping technology infrastructure running smoothly and efficiently.
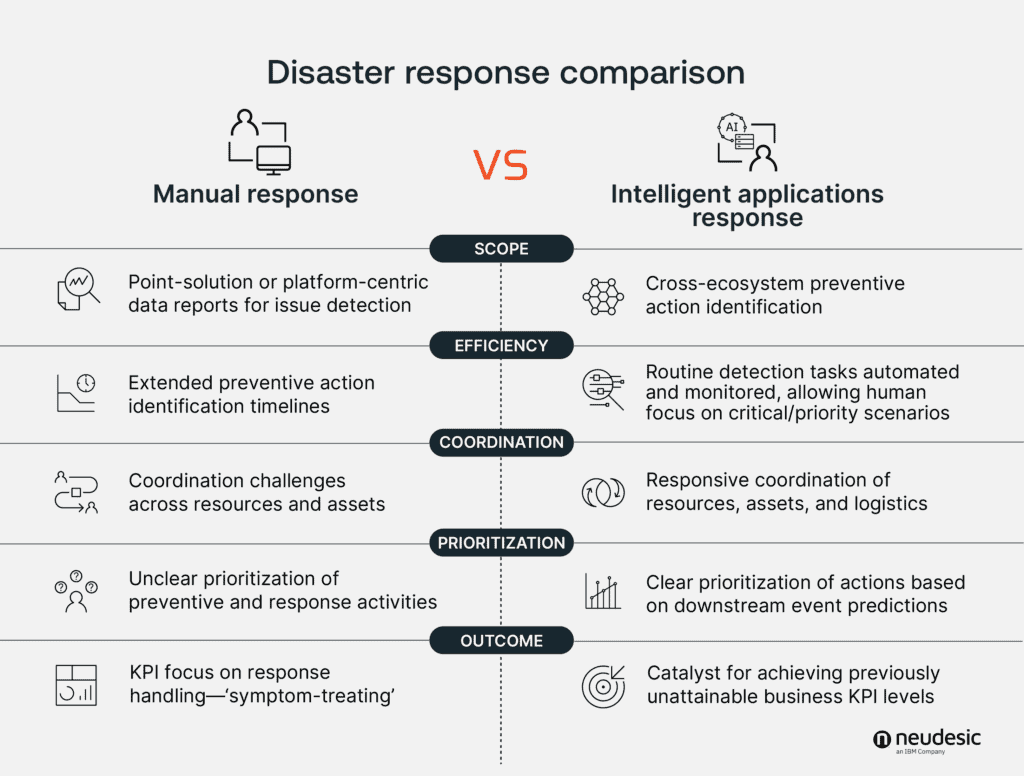
Comparing manual vs. intelligent application responses
Manual Response:
- Provide point-solution or platform-centric data reports for issue detection.
- Extends preventive action identification timelines.
- Suffer coordination challenges across resources, systems, and employees.
- Lack prioritization mechanism for preventive and response activities.
- KPI focus on response handling-‘symptom-treating’.
Intelligent Applications Response:
- Identify preventive actions across ecosystems.
- Detect tasks automated and remotely monitored, allowing human focus on critical/priority scenarios.
- Coordinate responses across resources, assets, and logistics.
- Prioritize actions based on downstream event predictions and business impact.
- Achieve previously unattainable business KPI levels.
- Monitor and manage network devices to ensure network integrity and security.
How intelligent applications integrate with technology infrastructure for disruption prevention and response strategies
IA is a natural inflection point toward Intelligent Operations (IntelOps), defined as the expansion of AI capabilities and performance measures across the greater IT enterprise. With intelligent operations, a collection of intelligent applications coordinate systems, interface with users, conduct root cause analysis, and take autonomous actions meant to improve the financial, security, and developer operations of an organization. In the next 18 months, we anticipate the growing use of Intelligent Ops within the back end of IT systems to fuel enterprise operations, creating new opportunities for disruption prevention and response. Intelligent apps can monitor the entire network to provide a comprehensive view of IT infrastructure and resources, ensuring immediate notifications for errors and long-term monitoring for predictive maintenance and resource planning. Additionally, these applications can help prevent security breaches by continuously monitoring for vulnerabilities and unauthorized access:
Routine autonomous maintenance
- Automation of maintenance and operations schedules.
- Autonomous remote repair, with or without human review.
Preventive autonomous maintenance
- Remote monitoring of equipment health, safety, and energy levels.
- Early/future outcomes prediction, paired with autonomous resolution.
Maintenance and incident response orchestration
- Response prioritization and coordination.
- Enhanced operational efficiency and SLA performance.
Crisis response
- Crisis response optimization across the workforce, assets, geolocation, and recommended actions.
- Recommendation engine for human review based on real-time events.
Incident and crisis aversion
- Response simulation.
- Response history, efficacy evaluation and integration.
- Autonomous mitigation recommendations and solution deployment with or without human review.
Industry use cases for disruption prevention by intelligent applications
Disruption emerges in different forms across industries, and so do pathways of effective prevention and response. Acting as a coordinating (vertical) or a collection of AI agents (horizontal), IA use cases feature the consistent theme of expanded usage of IT delivery to respond to events in real-time:
- Hospitality and travel: Responding to changing weather conditions and travel patterns with contactless updates to customers, facilitating high levels of customer satisfaction.
- Manufacturers: Facilitating accident-free workdays via wearables, improving factory uptime, and worker satisfaction. Intelligent apps can also help maintain and optimize technology infrastructure to improve factory uptime and worker satisfaction.
- Power and utilities: Identifying new early-warning data patterns across the IT ecosystem, mitigating the number of outage incidents.
Key intelligent application readiness considerations
There are four key considerations for assessing IA readiness within your IT organization. Use these discussion points with the readiness audit questions at the end of this blog to prompt engaging conversations across your team.
Preparing IT teams for the integration of intelligent apps is crucial to ensure they can deliver work efficiently and sustain high-quality performance.
Plan for scalable, responsive, and responsible AI across the IT ecosystem
Establishing a scalable AI infrastructure is the first step toward IA development. Disruption use cases, monitoring capabilities, evolving ML models, and feedback loops will drive large workload demands. A key factor in whether your current environment will grow seamlessly with IA will be readiness to support capabilities such as big data processing and complex ML models.
Responsive capabilities such as geolocation-based resource coordination should include a multitude of factors in prevention response beyond speed, including task sequencing, KPI fulfillment across scenarios, and solution cost efficiency. For example, IA can deploy recommendations that will drive overall system performance, differing from legacy siloss of maintenance. Testing IAs for cohesive responsive capability should be done rigorously to avoid unanticipated or unwanted outcomes.
Intelligent apps can automate routine tasks, allowing IT teams to focus on more productive tasks that add value to the organization.
Responsible AI is crucial. With IA response generation comes the potential for bias or misapplications in communication or recommended action. The ability to create traceable predictions and corrective action recommendations by both the workforce and automated delivery is key to ensuring IT departments stay in alignment with Responsible AI principles. It is vital to be able to understand how AI made both recommendation and response decisions.
Build in User Feedback Options to Strengthen Trust and Increase Value
Digital literacy and skills development will be core to the effective improvement of IA. System improvement will be contingent upon a workforce that understands how to interact, accept or reject recommendations, and continually engage with the IA platforms to improve the quality of disruption prevention and response.
With IA, the workforce can create a living, organic disruption prevention and response playbook. For IT departments, proper handling of feedback loops are critical to ensure the workforce believes that recommendations are representative of their collective best knowledge, versus unvetted system-generated content. The slightest misunderstanding in a prevention scenario can have negative consequences for AI trust. Feedback handling should cover variations in user communication and learning styles and even common accidental entries.
Establish data governance and safety protocols for recommendations, feedback handling, and security breaches
IA simulation and recommendation testing will drive new considerations for data governance. While preserving master data, IT will need to plan for where and how recommendations are stored and evaluated, including governance of user feedback loops. Guidelines to promote recommendations from sandbox environments to field deployment, filtering outlier and inaccurate feedback to avoid master data corruption, and new cybersecurity measures to prevent inadvertent points of entry are all considerations in maintaining enterprise safety. Additionally, protecting sensitive data from security breaches and unauthorized access through robust data governance and safety protocols is crucial to prevent the exfiltration of personally identifiable information (PII).
Expand the IT planning table with new collaborations and partnerships
IA integration will require elevated levels of engagement across technology collaborators and partners. Data sets, ML model training, user experience design, and platform integrations are just some of the areas in which strategic collaborations will improve disruption prevention and response. Exploring disruption use cases with ecosystem partners is a key action in opening the door for IA-aligned collaborations.
Questions for your intelligent applications readiness audit
Use these questions with your teams to better jumpstart conversations regarding IAs and their role in mitigating outages and reacting to disruptions in services:
- Is our technology, data, and AI infrastructure sufficiently flexible to support IA?
- What AI innovations are we exploring, and how can they be operationalized for disruption prevention and response?
- Can we create and support cross-platform integrations, user experiences, and data governance that deliver autonomous capabilities, decision-making prompts, and corrective feedback loops?
- Is our ecosystem sufficiently analytically advanced to support simulations and recommendation testing?
- How do we ensure Responsible AI delivery within our IA strategy?
- Do we have experience identifying, assessing, and rectifying low-quality or outlier information?
- Do we have the diversity in skill sets to manage IA strategy and execution?
- Do we need to change IT planning processes to ensure all voices are at the table for IA planning?
- What collaborations and partnerships should we explore as part of our IA strategy?
Enter the era of AI disruption prevention and response with confidence
Without a cohesive AI strategy, the modern enterprise risks fragmented disruption management. With a robust IA strategy, disruption prevention functions can look forward to optimized autonomous and human prevention activities with higher KPI performance. To fulfill the business needs, managing IA planning comes with a host of considerations across flexibility, innovation, feedback loops, and data governance. With proper planning, IA is the attainable next step in the progression of the intelligent enterprise. There are a few ways in which intelligent apps can optimize disruption prevention and response, such as through predictive maintenance and autonomous resolution. Responsive firefighting to disruptions is increasingly inefficient with advancing technological capability. With IA as coordinating agents, IT functions can deliver on speed, scale, and autonomy, enabling a healthier and more efficient enterprise.
As Microsoft’s US AI Partner of the Year and an emerging pioneer in intelligent operation deployments, Neudesic is uniquely positioned to help you explore these and many other possibilities. Contact us today to get started.
Related Posts